Some of you, who are in the aerospace industry, are probably familiar with a drill/countersink tool used in CNC manufacturing, to machine both the hole and the chamfer for the rivet head.
Did you know that with some modification, the same concept works also in manual operations? We’re here to tell you about it.
What is a Drill/Countersink tool?

A Drill/Countersink is a tool used mostly in CNC manufacturing of aerospace parts, with a purpose to machine both the required hole diameter and the relevant chamfer size for the rivet head. The tool can be made from PCD or CVD to be used for Composites. The drill head can be made from carbide and the countersink from PCD, to handle stack materials, such as C/Al or C/Ti.

The usage of a Drill/CSK sometimes limited in CNC from various reasons:
- It is not worthwhile preparing a jig for every part and machine it in CNC.
- In some cases, the drill entrance side, is not the same side the chamfer has to be made.
- When large part is about, there are concerns that along the part, you can not achieve the same chamfer size, due to minor part deflections in machining. In this case, drilling is done in CNC and countersinking later in manual operation at the assembly line.
While these circumstances limit the use of Drill/CSK in CNC, in assembly line, when all operations are done manually, the use of such a tools, does not exist so far.
What is the new concept?
Telcon developed a new concept of manual use Drill/CSK tools, which include 3 types of tools. All of them can be used manually with a thread connection to a standard stop-cage.

A Carbide Drill/CSK
Designed for C/C.
DKCC series.
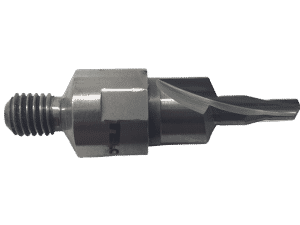
A PCD Drill/CSK
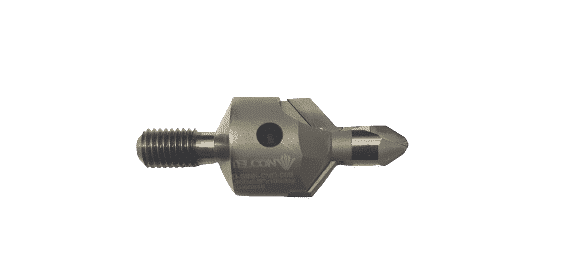
Designed for C/C
DKPC series.
A Carbide Drill/CSK
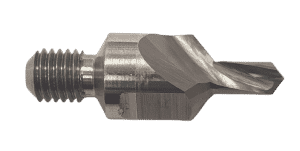
Designed for C/Al, Al/Al
DKCA series.
What are the benefits?
- Reducing number of operations – saving one or two operations and setups.
- Saving hourly costs.
- Reducing lead time of part manufacturing.
- Improving part quality – hole-chamfer concentricity is improved since both operations are done with the same tool.
Case study 1 – Composites/Composites:
Need to connect two panels of CFRP, with a thickness of 2.5+3.5mm.
Final hole diameter is 4.5mm with countersink angle of 100°.
| Current process steps | Improved process steps |
| Lower panel is drilled in CNC with 3.3mm pilot holes. | Lower panel is drilled in CNC with 3.3mm pilot holes. |
| Upper panel is temporarily glued to the lower panel | Upper panel is temporarily glued to the lower panel |
| A 3.3mm drill is manually used to drill 3.3mm holes also at the upper panel while the lower panel holes guide the way. | A stepped Drill/CSK (3.3/4.5/100°) series DKCC is manually used to create the final 4.5mm diameter and the 100° chamfer |
| A carbide 4.5mm drill is manually used to enlarge holes in both panels. | Riveting is used to connect both panels |
| A PCD countersink is manually used for the chamfer of 100° | |
| Riveting is used to connect both panels |
Summary: with the use of Drill/CSK, 2 operations and 2 setups were saved. In these parts there are 80 holes to drill. This means 2×80 = 160 times drilling operations. Practically, the customer is able finishing 6 parts a day instead of 4 parts with the previous process.
Case study 2 – Aluminum/Aluminum:
Need to connect two periphery panels of Aluminum, with a thickness of 1.6+1.8mm.
Final hole diameter is 4.0mm with countersink angle of 100°.
| Current process steps | Improved process steps |
| Lower panel is drilled in CNC with 2.5mm pilot holes. | Lower panel is drilled in CNC with 2.5mm pilot holes. |
| Upper panel is temporarily glued to the lower panel | Upper panel is temporarily glued to the lower panel |
| A 2.5mm drill is manually used to drill 2.5mm holes also at the upper panel while the lower panel holes guide the way. | A Drill/CSK (4.0/100°) series DKCA is manually used to create the final 4.0mm diameter and the 100° chamfer |
| A carbide 4.0mm drill is manually used to enlarge holes in both panels. | Riveting is used to connect both panels |
| A PCD countersink is manually used for the chamfer of 100° | |
| Riveting is used to connect both panels |
Summary: with the use of Drill/CSK, 2 operations and 2 setups were saved. In these parts there are at least 900 holes to drill only with this diameter. This means 2×900 = 1800 times drilling operations. Practically, the customer is able finishing manual operations on one part in 3 days instead of 5 days with the previous process.
